Understanding the differences between the different RAM types is essential when you want to upgrade a computer or build a new one. RAM is like the short-term memory of a computer. Just like our brains need to access information quickly to perform tasks efficiently, the CPU (Central Processing Unit) of a computer needs fast access to data in order to execute instructions effectively. When you open a program or a file, it gets loaded into RAM, allowing the CPU to quickly access and manipulate the data.
RAM is different from the long-term storage devices like hard drives or solid-state drives (SSDs). While these storage devices store data permanently even when the computer is turned off, this Memory is volatile and loses its data when the power is cut off. This is why it is called “random access” memory, as the CPU can access any piece of data stored in this Memory directly, without having to search through the entire storage device.
When a computer runs out of RAM, it starts using a portion of the hard drive or SSD as virtual memory, which is much slower than accessing data directly from RAM. This can lead to a noticeable decrease in performance, as the CPU has to wait longer for data to be retrieved from the slower storage device. This is why having enough Memory is crucial for smooth multitasking and running resource-intensive applications like video editing software or video games.
Upgrading the RAM in a computer is often one of the most cost-effective ways to improve its performance.
Types of RAM
There are several types available in the market, each with its own unique characteristics and specifications. Let’s take a closer look at the most common types:
DDR5
DDR5 RAM, also known as Double Data Rate 5 Random Access Memory, is the latest generation of RAM technology. It is an improvement over its predecessor, DDR4, offering faster speeds and increased bandwidth.
DDR5 RAM offers faster data transfer rates, allowing for quicker access to stored information. This is especially beneficial for tasks that require high-performance computing, such as gaming, video editing, and 3D rendering.
With its increased bandwidth, DDR5 RAM enables more data to be transferred simultaneously, resulting in smoother multitasking and better overall system performance.
DDR5 supports higher memory capacities, allowing for larger amounts of data to be stored and accessed quickly. This is particularly advantageous for applications that require large datasets, such as machine learning and data analytics.
DDR5 is designed to be more power-efficient compared to previous generations. It incorporates features like voltage regulation and power gating, which help reduce power consumption and heat generation.
DDR5 is not backward compatible with older DDR4 or DDR3 slots, as it requires a new motherboard that supports DDR5 technology. As of now, DDR5 RAM is relatively new and not widely available. However, it is expected to become more accessible as motherboard manufacturers release compatible models.
Overall, DDR5 RAM offers significant improvements in speed, bandwidth, capacity, and energy efficiency. As it becomes more prevalent in the market, users can expect better performance and enhanced computing experiences.
DDR4
DDR4, which stands for Double Data Rate 4, is the penultimate type of RAM in modern computer systems. It offers faster data transfer rates, lower power consumption, and increased memory capacity compared to its predecessors. DDR4 modules are compatible with motherboards that support DDR4 technology.
DDR4 has significantly improved performance compared to older RAM types. It is designed to operate at higher clock speeds, allowing for faster data access and transfer. This makes DDR4 ideal for demanding applications such as gaming, video editing, and graphic design.
In addition to its speed and performance, DDR4 also offers increased memory capacity. DDR4 modules can have higher densities, allowing for larger amounts of Memory to be installed in a single system. This is particularly beneficial for users who require a large amount of memory for multitasking or running memory-intensive applications.
Furthermore, DDR4 is designed to be more energy-efficient. It operates at lower voltages compared to DDR3, resulting in reduced power consumption. This not only helps to lower energy costs but also contributes to a greener and more sustainable computing environment.
DDR3
DDR3, or Double Data Rate 3, was the standard RAM type before DDR4 was introduced. It is still widely used in older computer systems and laptops. DDR3 modules offer decent performance and are compatible with motherboards that support DDR3 technology. However, they have slower data transfer rates and higher power consumption compared to DDR4.
DDR3 is a reliable and cost-effective option for users who don’t require the latest and greatest performance. It is suitable for everyday computing tasks such as web browsing, document editing, and multimedia playback. While DDR3 may not offer the same level of performance as DDR4, it can still provide a smooth and responsive user experience.
One advantage of DDR3 is its compatibility with older systems. Many older motherboards and processors are only compatible with DDR3, making it the only viable option for upgrading the memory in these systems. Additionally, DDR3 tends to be more affordable than DDR4 , making it a budget-friendly choice for users on a tight budget.
DDR2
DDR2, or Double Data Rate 2, is an older RAM type that is rarely used in modern computer systems. It has slower data transfer rates and lower memory capacity compared to DDR3, DDR4 and DDR5. DDR2 modules are compatible with motherboards that support DDR2 technology.
DDR2 was commonly used in computers from the mid-2000s to early 2010s. It offered improved performance compared to its predecessor, DDR, but was soon replaced by DDR3 due to its limitations. While DDR2 may still be found in older systems, it is not recommended for use in modern computers due to its outdated technology and limited compatibility.
DDR
DDR, or Double Data Rate, is an even older RAM type that is now considered obsolete. It has slower data transfer rates and lower memory capacity compared to DDR2, DDR3, DDR4, and DDR5. DDR modules are compatible with motherboards that support DDR technology.
DDR was widely used in computers during the late 1990s and early 2000s. It offered significant improvements in performance compared to its predecessor, SDR (Single Data Rate). However, DDR has long been surpassed by newer and faster RAM technologies, such as DDR2, DDR3, DDR4, and DDR5.
Due to its outdated technology and limited compatibility, DDR is no longer recommended for use in modern computer systems. Users looking to upgrade their RAM should consider DDR2, DDR3, DDR4, or DDR5 options, depending on the compatibility of their motherboard and the performance requirements of their applications.
As we can see in the previous image, the different types of RAM in appearance can be very similar, but in reality there are fundamental physical differences that prevent you from making a mistake and, for example, trying to install a DDR4 memory module on a motherboard. which only supports DDR5 memory. The different standards have a small gap in the connection area of the memory module, it is designed to avoid two specific scenarios:
- Avoid installing a RAM module in an unsupported socket.
- Install the memory module in the correct position.
RAM Brands and Manufacturers
There are multiple memory companies on the market, but only a few true memory manufacturing companies. When researching different memory brands, you may run across companies that claim to be memory manufacturers, when they’re really just module assemblers. How these companies work is that they purchase pre-manufactured parts (such as DRAM chips and printed circuit board) from true memory manufacturers, and then assemble these components to “manufacture” a module with their label on it.
True memory manufacturing involves a much higher level of technical expertise and quality control, and involves everything from selecting choice silicone to functional module testing. Memory manufacturers design, produce, and test components and modules at all stages of production. Memory modules consist of two pieces: DRAM semiconductor chips that store data, and printed circuit board (PCB), which connects the memory chips to the rest of the computer.
Technically, there are only a handful of semiconductor manufacturers with the capability to produce DRAM chips, and they are Micron (Crucial), Samsung, and Hynix. The companies that actually sell RAM take these modules and place them in their own PCB sticks.
That being said, there are several well-known brands that sell RAM. Each has its own distinct look, performance, price and compatibility with different types of motherboards. Here are all those major brands.
RAM Samsung
Samsung is one of the few companies that actually produce RAM, but that doesn’t make it the go-to brand for RAM. The company hasn’t really broken into the performance RAM market, and you would be hard-pressed to find a stick available. You could certainly find some laptop RAM, but that won’t be compatible with your desktop motherboard.
If you’re looking to upgrade an old laptop, then Samsung is a great option. The desktop sticks they have available are also good choices for server solutions.
RAM Micron
While they are good solutions for basic desktops or server solutions, this isn’t what you would want to put in a gaming PC. Micron memory doesn’t support XMP profiles (XMP is short for Extreme Memory Profiles. Essentially, RAM that supports that profiles can easily have the speed adjusted by switching to a different profile in the BIOS, which makes overclocking fast and simple), and it also lacks a lot of the heat spreaders found in gaming RAM products. Spreading heat is especially important in a gaming PC since most of the components will be pushed to their limits, creating a lot of heat.
Unless you’re upgrading a laptop or building some type of server, you will be better served by a different brand than Micron.
RAM Adata
ADATA has been around for a long time and is a staple budget brand for several PC components. The company offers regular RAM sticks that are great for standard desktops or servers, but the company also has an XPG line of gaming memory. XPG has the angular design for the heat spreader you would expect for a gaming product.
There are some compatibility issues with certain motherboards. Make sure you do your research to see if this product works with your board before buying.
RAM Crucial
Crucial is another budget brand for PC components, and the company also has RAM sticks available for sale. Crucial is owned by Micron, so it gets the benefit of having rigorous testing for and a direct line to its RAM modules. It’s also pretty affordable. There have also been reports of compatibility issues with certain MSI boards.
Kingston
Kingston is a well-known brand and perhaps one of the most popular in the entire world of technology for its reliable and high-quality RAM products. Here are some key points about Kingston RAM:
Product Variety: It has a wide variety of types of memories such as USB, microSD, RAM, among many more. Kingston offers a wide range of RAM products, from standard modules for desktop computers to high-speed modules for enthusiasts and gamers.
Compatibility: Their products are typically compatible with a variety of platforms and systems, making them a popular choice for memory upgrades.
Reliability: Kingston’s reputation is built on the reliability of its products. Their memory modules often have a long lifespan and good overall performance.
Warranty: Its guarantees range from one year, 5 years and some even for life. Kingston offers solid warranties on most of its products, providing peace of mind to users in case of issues or failures.
Prices: While not always the cheapest option, Kingston’s price-to-performance ratio is usually quite good due to its reputation and build quality.
Technologies: Kingston has been at the forefront of memory technologies from DDR to DDR5, offering options for different needs and budgets.
In summary, Kingston RAM is a solid choice for those seeking reliability, compatibility, and good performance in their computer systems.
Silicon Power
Silicon Power has gotten pretty popular over the years because it offers all the features gamers want in RAM at a reasonable price. The Zenith series has a premium aluminum heat spreader that improves performance and the overall lifespan of the product.
There is, of course, XMP support, so you can overclock these sticks and make your PC flashy in the process. The biggest drawback to Silicon Power is the out-of-box performance. Users have reported clock speeds that are lower than advertised, and they had to adjust settings in the BIOS to get those reported speeds. The good news is the RAM does perform as advertised, you just have to get it there yourself, which is less than ideal.
Patriot
Patriot makes some of the best RAM products around, and you can often find them in roundup lists when you search for the best RAM. Produced in the U.S., it also has great customer service support.
Patriot a significantly pricier option, but you’re getting a premium product at that price. You’re getting snappy speeds, excellent XMP performance, and RGB goodness in the package.
However, users have reported some issues with Patriot products. While customer service is great, customers have had their products arrive mislabeled, and sometimes they don’t work at all. Customer service is quick to replace these, but it does make it a hassle and a bit of an unnecessary annoyance to deal with.
Corsair
Corsair is one of the top names in PC accessories, and it makes a lot of peripherals including keyboards and gaming mice. Corsair is also the undisputed leader in gaming RAM. The Vengence line of RAM offers best-in-class performance, and Corsair undoubtedly has the best-looking products on the market.
Since Corsair is so popular it’s widely compatible with basically every motherboard brand. The components also include XMP 3.0 support with custom profiles also makes for a simple and powerful overlocking experience. Corsair provides the best RAM brand on the market.
Choosing the Right RAM
When it comes to choosing the right RAM for your computer, there are a few factors to consider:
1. Compatibility
First and foremost, ensure that the RAM you choose is compatible with your computer motherboard. Check the motherboard’s specifications to determine the type and maximum capacity of Memory it supports. Installing incompatible Memory can lead to system instability and performance issues.
2. Capacity
The capacity of RAM determines how much data your computer can store and access at any given time. If you use resource-intensive applications or multitask heavily, consider opting for higher capacity Memory modules. However, keep in mind that the operating system and software you use also have their own memory requirements.
3. Speed
The speed of RAM, measured in megahertz (MHz), determines how quickly data can be transferred to and from the memory. Higher Memory speed modules offer better performance, especially when running memory-intensive applications or gaming. However, the benefits of higher speed may not be noticeable in everyday tasks especially those that do not require too much memory or speed.
4. Budget
Lastly, consider your budget when choosing RAM. Higher capacity and faster Memory speed modules tend to be more expensive. Evaluate your needs and prioritize accordingly.
Additionally, it is worth mentioning that the type of RAM you choose can also affect its performance. There are different types of Memory available in the market, such as DDR3, DDR4, and DDR5. DDR4 is currently the most common and widely used type of RAM. It offers faster speeds and lower power consumption compared to DDR3.
Another factor to consider is the number of RAM slots available on your motherboard. Some motherboards have only two slots, while others may have four or more. If you have limited slots, it may be more cost-effective to purchase higher capacity RAM modules to maximize your available memory. On the other hand, if you have more slots, you can opt for lower capacity modules and add more RAM in the future if needed. Lastly, it is important to note that installing Memory is relatively easy and can be done by most computer users.
Installing RAM on PCs
Installing RAM on a PC is a relatively straightforward process. However, it is essential to follow the manufacturer’s instructions and take necessary precautions to avoid any damage to the components. Here’s a step-by-step guide to installing Memory:
1. Determine the Type and Capacity
Identify the type and capacity of Memory you need for your computer.
Refer to the motherboard manufacturer’s documentation or specifications to ensure compatibility.
It is important to note that different computers may require different types of RAM, such as DDR3, DDR4, or DDR5, and have different maximum capacities. Therefore, it is crucial to choose the right RAM to ensure optimal performance.

2. Power Off the Computer
Before installing or removing any hardware components, it is crucial to power off the computer and unplug it from the power source. This will prevent any electrical damage and ensure your safety. Additionally, it is recommended to ground yourself by touching a metal surface or using an anti-static wrist strap to prevent any static electricity discharge that could potentially damage the RAM or other components.
3. Locate the RAM Slots
Open the computer case, locate the RAM slots on the motherboard. Most desktop computers have multiple RAM slots. The slots are typically long, narrow slots with retaining clips or levers on the sides to secure the Memory modules in place.
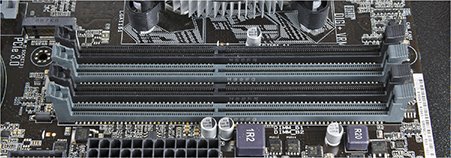

4. Remove Existing RAM (if applicable)
If you are upgrading the RAM or replacing existing modules, gently push the retaining clips or levers on the sides of the Memory slots to release the modules. Carefully remove the modules from the slots. It is important to handle the Memory modules with care, holding them by their edges to avoid any damage to the delicate electronic components.
5. Insert the New RAM
You must use good installation practices. Always store RAM sticks in antistatic packaging whenever they’re not in use, and use strict ESD handling procedures. Like many other pieces of the PC, RAM is very sensitive to ESD and other technician abuse. When holding the RAM, never touch the copper contacts with your fingertips, nor do you touch the Integrated Circuits. The correct way to grab the RAM is as we see in the image.
Hold the new RAM module by its edges, align the notch on the module with the key in the RAM slot, and insert it into the slot at a slight angle. Apply gentle pressure until the module clicks into place. It is crucial to ensure that the Memory module is inserted correctly and fully seated in the slot to establish a proper connection. Repeat the process for additional modules, if applicable.
6. Secure the RAM
Once the RAM modules are inserted correctly, push them down firmly until the retaining clips or levers snap into place. This ensures that the modules are securely installed and properly connected. It is important to ensure that the retaining clips or levers are fully engaged to prevent the RAM modules from becoming loose during operation.
7. Close the Computer Case
If you are working on a desktop computer, close the computer case and secure any screws or latches. This will ensure that the components are properly protected and that there are no loose connections.
8. Power On the Computer
After installing the RAM, reconnect the power source and turn on the computer. The system should detect the new RAM automatically. You can verify the installation by checking the system properties or using diagnostic software. It is recommended to check the BIOS settings to ensure that the new RAM is recognized and configured correctly. If the system does not detect the new RAM, double-check the installation to ensure that the modules are properly seated in the slots.
By following these steps, you can easily upgrade or replace the RAM in your PC, enhancing its performance and allowing for smoother multitasking and faster data processing.
Troubleshooting RAM Issues
While installing RAM is usually a straightforward process, you may encounter some issues along the way. Here are a few common problems and their possible solutions:
1. System Not Booting
If your computer fails to boot after installing new RAM, it may indicate compatibility issues or incorrect installation. Ensure that the RAM modules are properly seated in the slots and that they are compatible with your system. If the problem persists, try removing the new RAM and reinstalling the old modules to determine if the issue lies with the RAM itself.
2. System Instability or Crashes
If you experience system instability, crashes, or random error messages after installing new RAM, it may indicate faulty or incompatible modules. Remove the new RAM and reinstall the old modules to see if the problem persists. If the system stabilizes, consider replacing the new RAM or consulting a professional for further assistance.
3. Memory Compatibility Issues
In some cases, mixing different types or speeds of RAM modules can cause compatibility issues. It is generally recommended to use RAM modules of the same type, capacity, and speed for optimal performance. If you need to mix RAM modules, ensure that they are compatible and consult the motherboard’s documentation for guidance.
4. Insufficient RAM
If your computer is running slow, freezing, or struggling to handle resource-intensive tasks, it may indicate insufficient RAM. Consider upgrading to higher capacity modules to improve system performance. However, keep in mind that other factors, such as the processor and storage, also affect overall performance.
Additional factors that can contribute to RAM issues include improper voltage settings, outdated BIOS, or faulty motherboard slots. It is important to ensure that your BIOS is up to date and that the RAM is receiving the correct voltage. Checking the motherboard’s manual or manufacturer’s website can provide guidance on the correct voltage settings for your specific RAM modules.
If you have exhausted all troubleshooting options and are still experiencing RAM issues, it may be necessary to consult a professional technician. They can perform a thorough diagnosis of your system to identify any underlying hardware or software problems that may be affecting the RAM’s performance.
Remember that RAM plays a crucial role in the overall performance of your computer. It is essential to address any issues promptly to ensure optimal performance and avoid potential data loss or system instability.